In the gaming world, one of the key elements ensuring smoothness and immersion is the compatibility between the monitor and the graphics card. G-Sync and FreeSync technologies represent breakthrough solutions, eliminating issues such as screen tearing and input lag. In this article, we will discuss how to configure these technologies in 2024, highlighting their differences and providing practical steps to achieve optimal performance.
What is G-Sync?
The majority of gaming monitors available today come equipped with technology that synchronizes the refresh rate of the display with the frames per second generated by the graphics card. The idea is that the monitor will display exactly the frames currently generated by the graphics card, eliminating issues when, for example, the monitor has a 144Hz refresh rate, but the graphics card can only produce 80FPS. The goal is to eliminate common problems like screen tearing and reduce input lag. Currently, the most popular options in monitors are NVIDIA’s G-Sync and AMD’s FreeSync.
Both technologies operate on a similar principle and are based on the Adaptive-Sync technology from VESA. The main difference is that G-Sync monitors require a special chip installed, and you need an NVIDIA graphics card. Monitors with FreeSync or Adaptive-Sync do not require any special chip. Interestingly, many AMD FreeSync or Adaptive-Sync monitors can also be used with NVIDIA graphics cards, despite the „AMD” name suggesting compatibility only with red graphics cards.
As shown in the image below, even though I have an NVIDIA graphics card, I still use AMD FreeSync technology on my second monitor.
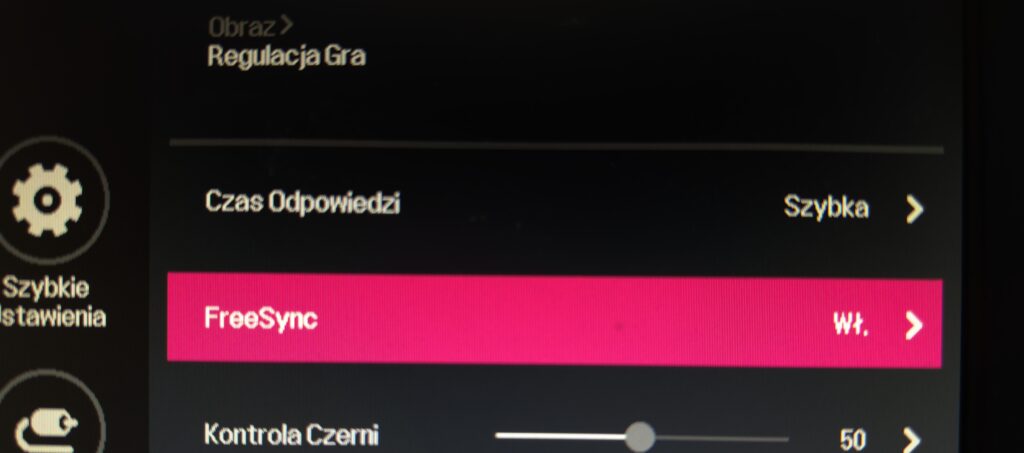
G-Sync, FreeSync, or G-Sync Compatible Monitor
There are several options available in the market, including G-Sync, G-Sync Ultimate, G-Sync Compatible, AMD FreeSync, AMD FreeSync 2. Each option differs, usually in the variable refresh rate range, e.g., a G-Sync Ultimate monitor may have a range of 1-240 Hz, whereas G-Sync Compatible may offer a range like 48-240 Hz. Faster synchronization also often comes with a higher price tag.
In my opinion, the most recommended option is a monitor equipped with G-Sync Compatible technology, assuming you have an NVIDIA graphics card. This is a monitor that has Adaptive-Sync technology and has undergone a special test by NVIDIA to receive certification. NVIDIA estimates that only 5% of available Adaptive-Sync monitors pass this rigorous test, but in reality, many uncertified monitors perform well in this task. Unfortunately, we cannot guarantee this.
In the example configuration presented, I will use my personal monitor equipped with G-Sync Compatible – the LG UltraGear 27GN800P-B 27″ 144Hz.
Official list of certified monitors: nvidia.com
Recommended monitors: FPSForge.com
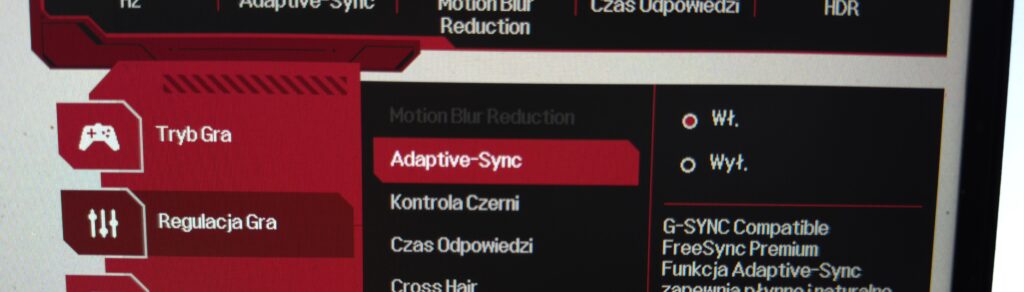
How to Enable G-Sync
First, we need to enable G-Sync on our monitor, and depending on the technology used, it may have a different name. In my case, it was „Adaptive-Sync,” as seen in the previous screenshot.
Next, we must launch the „NVIDIA Control Panel” and go to the „Set up G-SYNC” tab
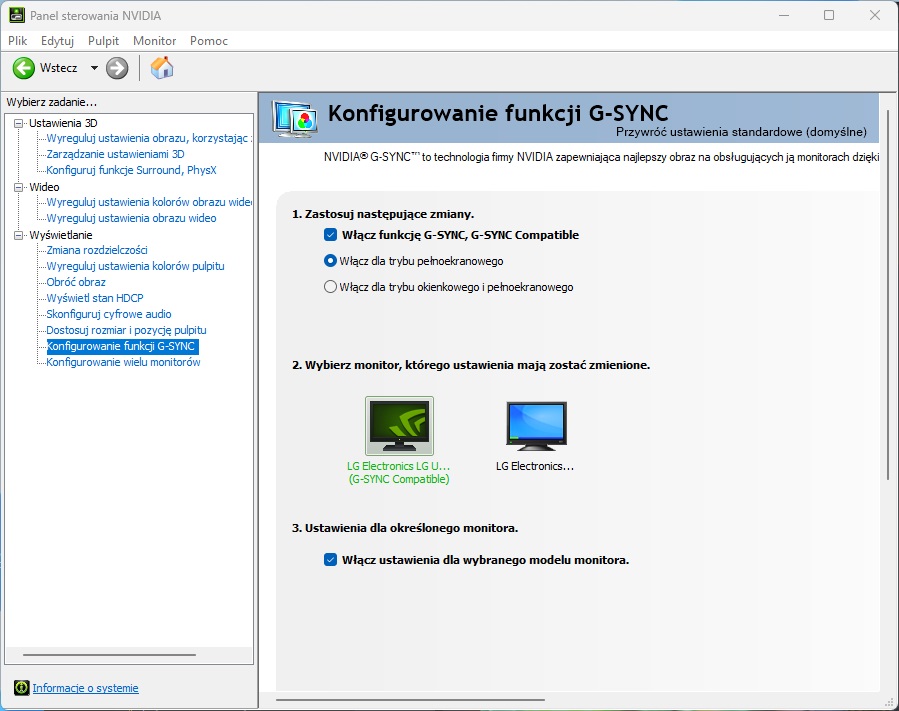
Here, I recommend selecting the option „Enable G-SYNC, G-SYNC Compatible” and set it to work only for the fullscreen mode. Unfortunately, the second option may cause various problems, so when using G-Sync technology, we are forced to use fullscreen mode in games.
Correct G-Sync Configuration
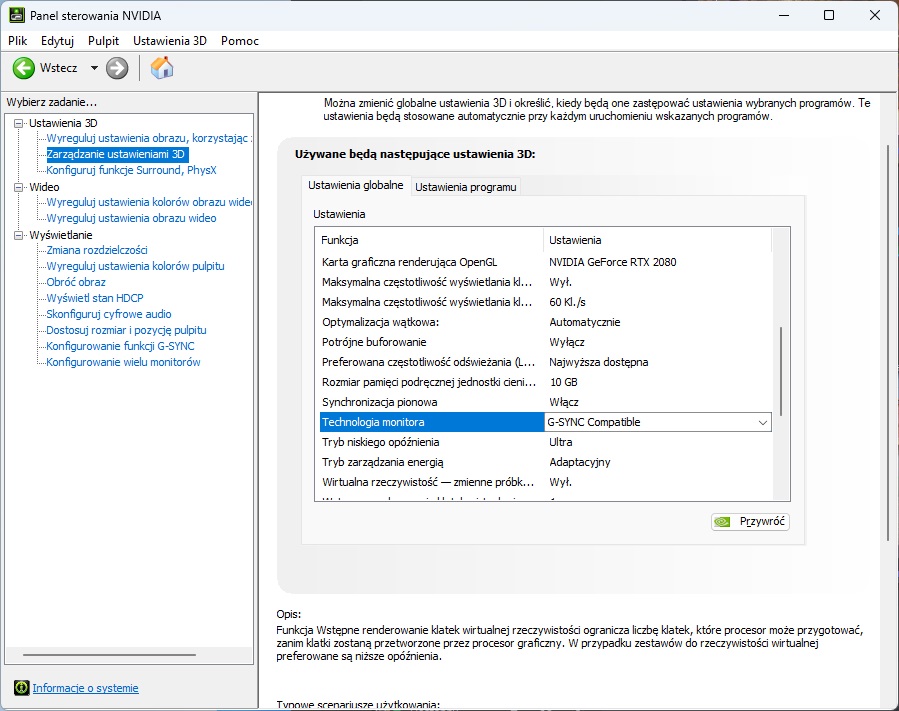
In the „Manage 3D Settings” tab, we need to adjust a few settings. One of them may seem controversial:
- Monitor Technology: G-SYNC Compatible
- Low Latency Mode: Ultra
- Vertical Sync: On
Vertical Sync, disliked by most of us, works differently when used with G-Sync technology. It no longer causes the issues we experienced in the past, where it was common to turn it off first. Thanks to synchronization, our FPS is capped slightly below the refresh rate of our monitor, e.g., at 144 Hz, the locked FPS would be 138-139. Theoretically, we can manually set this by adjusting the lock in the settings of the game, NVIDIA settings, or an external application like Rivatuner Statistic Server. However, based on my experiences, using vertical synchronization is better. V-Sync should be enabled in the control panel but disabled in the game settings!
Set the Low Latency Mode to Ultra to reduce the time it takes for the computer to process the generated frame and display it on the monitor. The successor to this technology is NVIDIA Reflex, which must be enabled in the game if it includes it. (NVIDIA Reflex automatically „overrides” the low latency mode and works significantly better). Set NVIDIA Reflex to On+BOOST, or On if your computer cannot generate the required number of frames.
Summary
Configuring G-Sync and FreeSync can be a crucial factor influencing the quality of gaming experiences. When choosing between G-Sync, FreeSync, or the G-Sync Compatible option, it’s essential to understand the benefits they offer and how to configure them correctly. Properly adjusted settings, such as enabling vertical synchronization or low latency mode, can significantly improve game smoothness and minimize delays. Discover how to make the most of synchronization technology and follow the steps that will make your gaming experiences even more satisfying.




1 Response
[…] Dynamic Sync Technology. Sync technology eliminates screen tearing during dynamic gameplay. G-SYNC or FreeSync technologies are beneficial, and their configuration is detailed in the provided article: How to Properly Configure G-Sync and FreeSync in 2024 […]